US Scientists Develop BISC: Ultra-Thin Neural Implants with Wireless Brain-Computer Interface
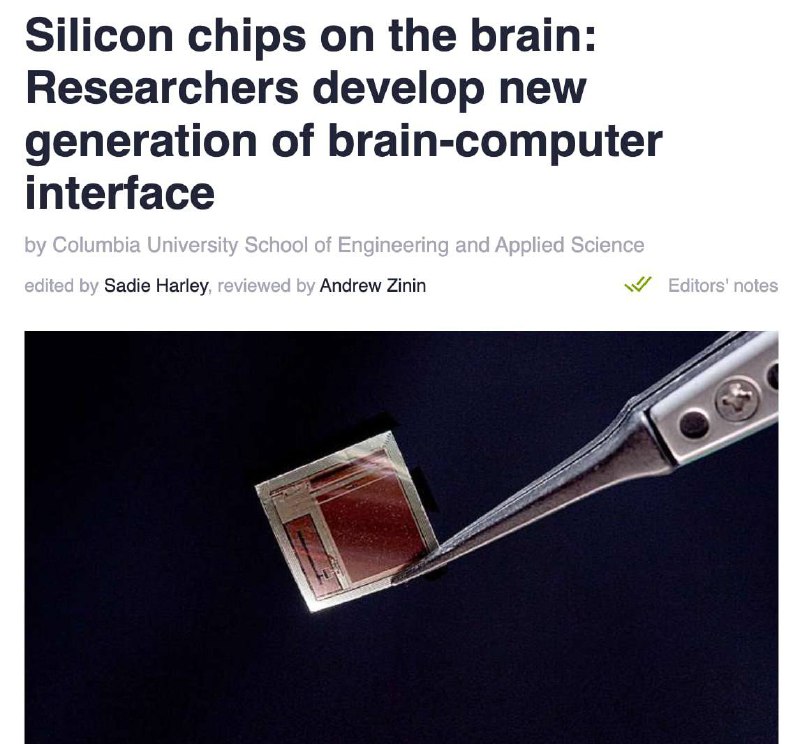
Researchers from the United States have developed a next-generation neural implant technology called BISC (Brain-Integrated Sensing and Communication). These innovative devices are designed to be positioned in the subdural space between the brain and skull, offering a significantly less invasive installation procedure compared to existing solutions like Neuralink.
The implant features an ultra-thin form factor, approximately the thickness of a human hair, and establishes wireless connectivity with external devices via Wi-Fi protocol. This architecture enables real-time bidirectional data transmission between the brain and computer systems, facilitating immediate signal processing and response.
The technology demonstrates promising therapeutic applications across multiple neurological conditions, including:
• Epilepsy management through seizure detection and intervention
• Spinal cord injury rehabilitation via neural pathway restoration
• Vision restoration for patients with blindness
The BISC platform has successfully completed preclinical validation studies, and initial human trials have already commenced, marking a significant milestone in the development of minimally invasive brain-computer interface technologies.